RDF Business
Holder of RDF Manufacturing Equipment Patent
RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) is converting waste into solid fuel. This involves removing non-combustible materials such as metals and glass from municipal waste, construction debris, and food waste. The remaining material is then shredded and dried to create low-emission solid fuel.
Technology Details
-
①
Waste typically cannot be stored for long periods due to decomposition, but RDF can be stored for extended durations without decay by removing moisture.
RDF is highly compressed into chalk-like shapes, making it easy to transport. It also features uniform calorific value and size, enabling the automation of handling processes. -
②
RDF has a calorific value of 4,000-5,000 kcal/kg, making it a cost-effective fuel that can be sourced domestically from waste.
RDF made from waste plastic, known as RPF (Refused Plastic Fuel), has a higher calorific value of 6,000-8,000 kcal/kg compared to the average calorific value of domestic anthracite coal, which is around 4,000 kcal/kg. -
③
By mixing neutralizing agents during the production of RDF, harmful gas emissions can be significantly reduced compared to the direct incineration of waste. However, RDF must be burned as a solid fuel in combustion equipment with pollution control devices.
Dust filtration and air circulation systems are installed in RDF processing plants to manage the excessive odor and dust generated during RDF production.
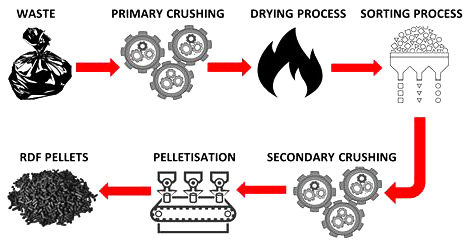
Process Technology
- ①
Crushing Technology : By utilizing crushing technology to break down raw materials into smaller particles, waste compression becomes easier while increasing the waste density, surface area exposed to air, and combustion speed. The crushed materials are also easier to mix and burn. Adopting graded crushing technology helps group fuel particles more effectively, which enhances energy utilization during waste incineration power generation.
- ②
Sorting Process: : Efficient sorting technology improves the purity of raw materials and boosts the fuel's calorific value. For instance, magnetic separators can remove metal impurities, while adsorbents can separate combustible components, further increasing the RDF's calorific value.
- ③
Compression Molding Technology : Advanced compression molding technology minimizes the internal voids in fuel pellets, optimizes the combustion surface area, and enables more complete combustion, thus increasing calorific value. Additionally, particle quality control technology ensures a uniform combustion surface area, improving combustion efficiency.
 Pre and Post-Crushing of Household Waste
Pre and Post-Crushing of Household Waste
Manufacturing Process
- Step.01Sorting
- Step.02Coarse
Crushing - Step.03Magnetic
Separation - Step.04Air
Classifier - Step.05Fine
Crushing - Step.06Carbonization

Cost Reduction Effects in Waste Treatment
- The current cost for waste incineration ranges from 120,000 to 170,000 KRW per ton (based on 100 tons).
- Using RDF machinery reduces processing costs to 80,000 to 100,000 KRW per ton, resulting in savings of 40,000 to 70,000 KRW per ton.
- This leads to daily savings of 4 to 7 million KRW, monthly savings of 100-175 million KRW and annual savings of 1.2-2.1 billion KRW.
- Additional revenue is also generated from solid fuel sales.
Other Spillover Effects
- Energy recovery analysis shows that approximately 76.6% of electricity consumption for RDF production can be recovered.
- As outlined in the Ministry of Environment's comprehensive waste-to-energy plan, significant job creation is expected in sectors such as construction, operations, incineration facilities, and technology development.
- Developing central and individual heating systems for industrial, residential, and horticultural use is also anticipated.
- Leading to further job creation.
Overseas Sales
-
MOU regarding RDF with the Republic of South Africa
-
Solar energy and RDF consulting services in Oman and Indonesia
-
Solar energy and RDF consulting services in Kenya
-
Solar energy and RDF consulting services in Nigeria




















